How to Master Open-Source Intelligence: Tips and Tricks
Open-Source Intelligence is the practice of gathering and analysing publicly available data to gain actionable information. Even if you are a cyber security professional, journalist, or simply someone curious about investigative techniques, mastering Open-Source Intelligence allows you to uncover comprehensive data and make informed decisions through ethical analysis. This article “How to Master Open-Source Intelligence: Tips and Tricks” will explore the Open-Source Intelligence cycle, compare active and passive techniques, give real-world examples, and offer tips and tricks for staying updated in this dynamic field.

What is Open-Source Intelligence?
Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) refers to the collection and analysis of publicly available information. This includes data from social media, websites, public records, news articles, and more. By using OSINT techniques and leveraging relevant tools, individuals can uncover a wealth of information about their subject.
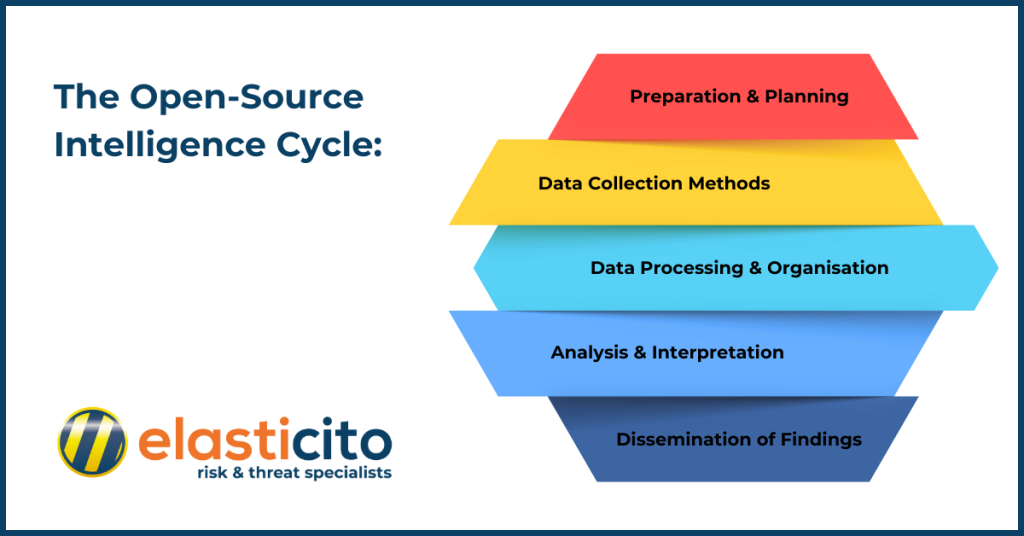
The Open-Source Intelligence Cycle:
1. Preparation and Planning
The journey begins with a well-defined plan. Just like any good detective story, you need to know the who, what, when, where, why, and how. Let’s begin by outlining the intelligence requirements and crafting a comprehensive plan to achieve them. Once the plan has been crafted, it undergoes a critical review and approval process by a team lead or director.
2. Data Collection Methods
Upon approval of the plan, analysts begin carefully collecting OSINT data to fill the intelligence requirements. This can often be the longest step, as many analysts rely on manual methods for collection. Managing online footprints and documenting findings can slow down the process. Depending on the information’s location and accessibility, analysts may spend momentous time collecting and archiving relevant data.
3. Data Processing and Organisation
After data collection, it must be analysed and processed. This could involve removing false positives and evaluating source credibility and reliability. At this stage, analysts interpret the collected data to prepare it for incorporation into final products. More validation and contextualisation may be needed to frame the information appropriately.
4. Analysis and Interpretation
After processed, the data can be categorised and prioritised for use in final intelligence products. This often involves distilling the information into a concise, simplified product that can be briefed or presented to the team lead. Building on this foundation, OSINT is often integrated or fused with other intelligence to develop a more complete product. Furthermore, analysts may also provide insights or commentary to lend expertise and perspective.
5. Dissemination of Findings
The ultimate step involves delivering the intelligence products to the intended audience, typically the individual who started the cycle. Dissemination to a broader audience may occur depending on the intelligence reports and the operation’s goal. For OSINT, issuing the product to a wide audience is often a key goal, as the information can be easily shared across organisations and partner nations. The urgency and speed of dissemination depend on the information’s nature; indications and warnings would take higher priority over a weekly update brief. Evaluation and feedback are likely to occur prominently at this stage but are often observed throughout the other steps as well. Once complete, the intelligence cycle can be repeated for the next product.
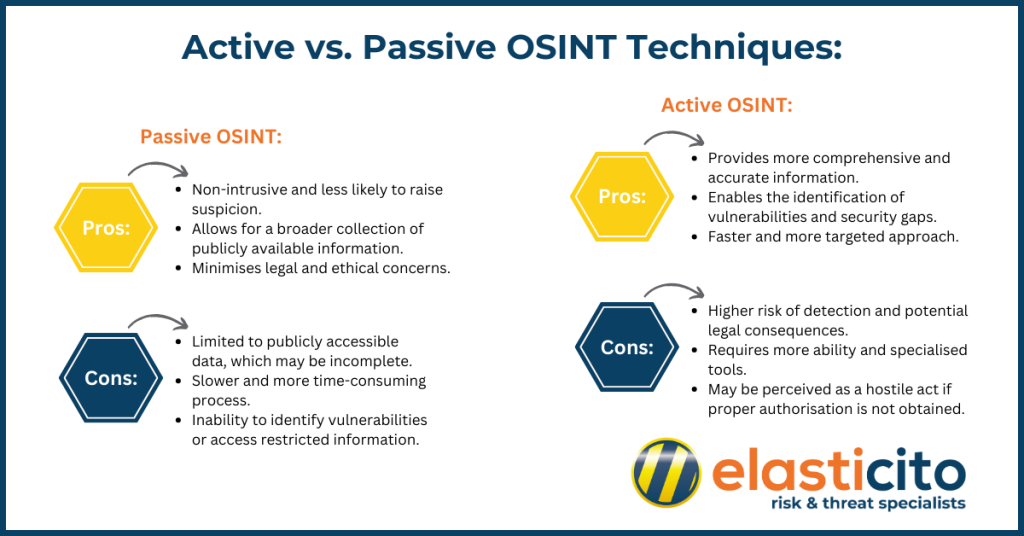
Active vs. Passive OSINT Techniques:
What is Passive OSINT?
Passive OSINT refers to the collection of publicly available information without directly engaging or interacting with the target. It involves gathering data from sources like online news articles, public social media posts, and websites, without revealing one’s presence or intentions to the subject of interest. The key aspect of passive OSINT is that the researcher remains invisible and undetected, quietly absorbing information like a fisherman casting a wide net.
Some examples of passive OSINT techniques include:
- Monitoring public social media profiles and posts.
- Analysing news articles and reports.
- Reviewing publicly available documents and databases.
- Conducting general web searches and browsing.
The main advantage of passive OSINT is its non-intrusive nature, allowing analysts to gather intelligence without raising suspicion or triggering alarms. However, passive techniques are limited to publicly accessible information, which may not provide a complete picture of the target.
What is Active OSINT?
Active OSINT involves directly engaging or interacting with the target system or individual to gather information. This is a more aggressive approach which requires the use of tools and techniques that actively probe the target. These tools may include port scanning, vulnerability scanning, or trying to gain access through password cracking.
Examples of active OSINT techniques include:
- Sending friend requests or messages on social media platforms.
- Downloading files or documents from a target’s website or blog.
- Conducting network mapping or port scanning.
- Attempting to access restricted or obscured information.
Active OSINT can provide more comprehensive and exact information about a target’s security posture. However, it also carries a higher risk of detection, as the target’s intrusion detection systems (IDS) or intrusion prevention systems (IPS) may identify the reconnaissance activities.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach:
Both passive and active OSINT techniques have their advantages and disadvantages. These should be carefully considered based on the specific requirements and goals of the investigation.
Passive Open-Source Intelligence:
| Pros: | Cons: |
|
|
Active Open-Source Intelligence:
| Pros: | Cons: |
|
|
The choice between passive and active OSINT techniques depends on many variables. These may include the nature of the investigation, time constraints, available resources, and the level of risk an organisation is willing to accept. In some cases a combination of both approaches may be necessary to gather comprehensive intelligence while minimising risks.
Real-World Examples of OSINT Usage:
First Case Study: Cyber security
From tracking global trade disruptions caused by the Suez Canal blockage to exposing criminals and aiding law enforcement, OSINT is proving its worth in various critical situations. This case study highlights the effectiveness of OSINT in real-time crisis response, uncovering complex criminal networks, streamlining investigations, and offering valuable insights for law enforcement.
Second Case Study: Market Research
Market research doesn’t have to break the bank. OSINT empowers organisations to use free online resources for valuable intel on target markets, competitors, trends, and consumer preferences. This data fuels data-driven decisions, finds ideal demographics, and uncovers competitor strategies. By analysing website traffic and consumer feedback through OSINT tools, marketers can optimise campaigns, tailor content for maximum engagement, and achieve superior brand visibility.
Third Case Study: Academic Research
Uncover the secrets of the “OSINT market” with the industry’s most comprehensive report (2023). Gain insights into market size, segmentation (type, application, user, region), growth drivers, and future trends. Analyse regional influences and opportunities across the US, Europe, Asia, and more. Understand how factors like COVID-19 and global conflicts affect the market. Make informed decisions and propel your growth strategy with this powerful market intelligence.
Staying Updated in the OSINT Field:
Staying updated in the rapidly evolving field of OSINT is crucial for professionals to maintain their skills and knowledge. Here are some effective strategies to stay informed:
Training and Certification Programs
Pursuing OSINT training and certification programs can help professionals enhance their expertise and stay current with the latest techniques and methodologies. One such program is the Certified in Open-Source Intelligence (C|OSINT), offered by Tonex. This globally recognised and accredited certification provides real-world applicable skills used by law enforcement, military intelligence, private investigators, and cyber security professionals.
Numerous other online courses and certifications are also available which cover various aspects of OSINT. This includes social media investigations, Dark Web exploration, and data analysis. These programs offer firsthand labs and practical exercises. Participants can gain practical experience in addition to theoretical knowledge.
OSINT Communities and Forums
Joining active OSINT communities and forums is an effective way to stay informed and engage with fellow professionals. These platforms ease knowledge sharing, allow participants to ask questions, and provide opportunities to gain experience from the experiences of others. By actively taking part in these communities, professionals can gain insights into emerging trends, new tools, and best practices.
Popular OSINT communities and forums include
- OSINT subreddit on Reddit.
- OSINT Twitter community.
- OSINT-focused Discord servers.
- OSINT-related forums and discussion boards.
- Keeping abreast of New Tools and Techniques.
The OSINT landscape is constantly evolving, with new tools and techniques appearing regularly. To stay ahead of the curve, professionals should:
- Follow relevant OSINT blogs and websites for the latest updates and resources.
- Use Twitter’s search bar and follow pertinent keywords or hashtags related to OSINT.
- Create a dashboard using tools like Tweetdeck to track OSINT content.
- Attend virtual or in-person conferences, webinars, and meetups focused on OSINT.
- For Third-Party Risk Monitoring, solutions like Black Kite, make extensive use of OSINT.
- If you require assistance with OSINT, Elasticito offers expertise in this field.
By staying updated with the latest tools, techniques, and trends, professionals can ensure they are equipped with the most up-to-date information and resources to excel in their OSINT endeavours.
Conclusion:
Open-Source Intelligence presents both challenges and opportunities for professionals across diverse fields. Mastering OSINT techniques, whether passive or active, equips individuals with the ability to navigate the vast expanse of publicly available information and extract invaluable insights. By harnessing the power of OSINT, organisations can enhance their cyber security posture, gain a competitive edge in market research, and contribute to groundbreaking academic studies.
As the OSINT community continues to grow and innovate, it is crucial to stay abreast of emerging tools, methodologies, and best practices. Engaging with OSINT communities, pursuing certifications, and attending industry events can foster a deeper understanding of this dynamic field. Embracing OSINT as an invaluable resource can empower professionals to make informed decisions and drive impactful change in their respective domains.
Contact Elasticito today to learn more about unlocking the full potential of OSINT for Cyber Risks and fortifying your organisation’s defences.
