How to Achieve Cyber Resilience Using the NIST Cybersecurity Framework

In today’s digital age, cyber threats pose significant risks to organisations of all sizes. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework has emerged as a crucial tool to help businesses enhance their cyber resilience. This comprehensive approach to risk management provides a structured method to assess, improve, and maintain an organisation’s cyber security posture. By adopting this framework, companies can better protect their assets, data, and reputation from ever-evolving digital threats. The article will explore the key components of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and how it helps to boost cyber resilience. It will delve into the importance of cyber resilience in the current digital landscape and outline practical steps to put the framework into action. By the end, readers will gain valuable insights on how to use this powerful tool to strengthen their organisation’s defences against cyber attacks and build a more resilient digital infrastructure.
The Importance of Cyber Resilience in Today’s Digital Landscape
In today’s hyper-connected world, cyber resilience has become a critical necessity for organisations of all sizes. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats pose significant risks to businesses, making it essential to develop robust strategies to protect assets, data, and reputation.
Evolving Threat Landscape
The cyber security landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years. Cyber risks are skyrocketing, with an alarming 83% of organisations experiencing more than one data breach during 2022. The total number of ransomware attacks surged by 13%, a rise equal to the last five years combined. This surge in cyber incidents highlights the urgent need for enhanced cyber resilience.
Threat actors are constantly adapting their tactics and techniques to exploit new vulnerabilities and maximise their gains. The development of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and large language models (LLMs), has introduced additional complexities to the threat landscape. While these technologies have beneficial applications, they can also be used for malicious purposes, such as spreading misinformation and conducting cyber attacks.
Business Impact of Cyber Incidents
The impact of cyber incidents on businesses can be severe and far-reaching. A successful cyber attack can have devastating consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, legal liabilities, and regulatory fines.
- Financial Impact: In 2022, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.35 million, while in the U.S., it averaged $9.44 million. These expenses can include ransom payments, lost revenues, business downtime, remediation, legal fees, and audit fees.
- Stock Market Performance: Publicly traded companies suffered an average decline of 7.5% in their stock values after a data breach, coupled with a mean market cap loss of $5.4 billion. On average, companies experiencing a significant data breach incident underperform the NASDAQ by 8.6% after one year, and this gap can widen to 11.9% after two years.
- Supply Chain Disruption: The impact of a cyber incident can reverberate throughout the entire supply chain, causing up to 26 times the loss for a company’s business ecosystem. For example, a ransomware attack on ION Trading Technologies sent financial institutions scrambling to confirm trades manually.
- Credit Rating Impact: Cyber risks can result in credit-rating downgrades, impacting a company’s ability and cost to secure financing. Moody’s announced in 2018 that it would evaluate companies’ cyber security practises when assigning credit ratings.
To mitigate these risks, organisations must prioritise cyber resilience. This involves developing comprehensive incident response plans, implementing robust business continuity and disaster recovery strategies, and continuously monitoring and updating security measures. By demonstrating cyber resilience, companies can maintain customer trust and loyalty, even in the face of security breaches, and stay ahead of emerging threats in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Key Components of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework consists of five core functions that work together to help organisations build a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. These functions are designed to be carried out concurrently and continuously to form an operational culture that addresses cyber risks.
Identify
The Identify function helps organisations develop an understanding of how to manage cyber security risks to systems, people, assets, data, and capabilities. This involves conducting an audit to determine which systems are vital for operations. By identifying physical and software assets, understanding the business environment, and recognising cyber security policies, organisations can focus and prioritise their efforts.
Protect
The Protect function outlines appropriate safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical infrastructure services. It involves implementing cyber security safeguards and practises to prevent or lower the chances of harmful incidents. Key aspects include identity management, access control, awareness and training, data security, and protective technology.
Detect
This function defines activities to identify the occurrence of a cyber security event promptly. It emphasises the importance of continuous monitoring and threat hunting to identify unusual activity or anomalies. Organisations should implement security continuous monitoring capabilities and maintain detection processes to provide awareness of anomalous events.
Respond
The Respond function includes activities to take action regarding a detected cyber security incident. It supports the ability to contain the impact of a potential incident. Key components include response planning, communication, analysis, mitigation, and implementing improvements based on lessons learned.
Recover
The Recover function identifies activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore capabilities or services impaired due to a cyber security incident. It supports timely recovery to normal operations to reduce the impact of an incident. This involves implementing recovery planning processes, making improvements based on lessons learned, and coordinating internal and external communications during and after recovery.
By implementing these five core functions, organisations can build a resilient, “antifragile” business model that anticipates, resists, and recovers from adverse and unexpected events.
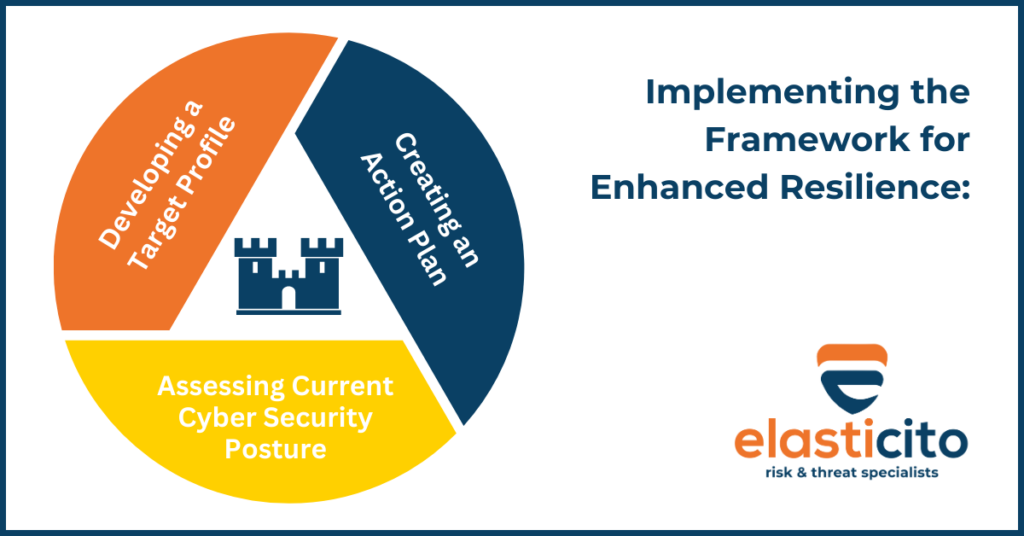
Implementing the Framework for Enhanced Resilience
Assessing Current Cyber Security Posture
To implement the NIST Cybersecurity Framework effectively, organisations must first assess their current cyber security posture. This involves creating a Current Profile that specifies the cyber security outcomes the organisation is currently achieving. The assessment process includes taking an inventory of all system components, from network switches to machine tools, and determining the necessary information to account for each component.
Developing a Target Profile
Once the current posture is established, organisations should develop a Target Profile. This profile specifies the desired cyber security outcomes that align with the organisation’s risk management objectives. The Target Profile should consider business requirements, risk tolerance, and available resources. It’s crucial to involve executives in gathering information about organisational priorities and risk direction.
Creating an Action Plan
The final step involves creating a comprehensive action plan to bridge the gap between the Current and Target Profiles. This plan should prioritise cyber security improvements based on business needs and risk management processes . Key components of the action plan include:
- Gap Analysis: Gap Analysis identifies and analyses the differences between the Current and Target Profiles.
- Prioritisation: Consider mission drivers, benefits, risks, and necessary resources when prioritising actions.
- Implementation: Execute the plan, focusing on achieving risk targets through common services, controls, and collaboration.
- Monitoring: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and key risk indicators (KRIs) to track progress.
By following this structured approach, organisations can enhance their cyber resilience and adapt to evolving threats. It’s important to note that cyber resilience requires a systematic, structured, and adaptive approach led by the C-suite and board, rather than being relegated solely to the IT department.
Conclusion
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework has a significant influence on enhancing cyber resilience in today’s digital landscape. By adopting its five core functions – Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover – organisations can build a strong defence against cyber threats. This structured approach enables businesses to assess their current cyber security posture, develop targeted improvements, and maintain a resilient digital infrastructure.
To implement the framework effectively, companies need to create a comprehensive action plan. This involves assessing the current state, setting clear goals, and prioritising improvements based on business needs and risk management processes. By following this systematic approach, organisations can adapt to evolving threats and protect their assets, data, and reputation. In the end, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework serves as a valuable tool to strengthen an organisation’s defences and build a more secure digital future.
Interested to learn more about the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and how to implement it in your business? Contact the team at Elasticito. We’d be happy to discuss your requirements.
