8 Surefire Shields Against Ransomware
In our increasingly digital world, data is the cornerstone of our lives. It stores everything from personal photos to financial records, and for organisations, it is the engine that keeps operations running. But with this dependence comes a growing threat: Ransomware. This malicious software acts like a digital kidnapper, encrypting your files and holding them hostage until a ransom is paid. Ransomware attacks can be devastating. By scrambling your data, they can grind organisations to a halt, leading to lost revenue and damaged reputations. For individuals, the impact can be just as severe, with cherished memories and important documents locked away. This can be a devastating blow to individuals and organisations alike, resulting in financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Read our blog, “8 Surefire Shields Against Ransomware”, to help you keep your data safe.

Understanding the Enemy: How Ransomware Operates
Before diving into defensive strategies, it is crucial to understand how Ransomware works.
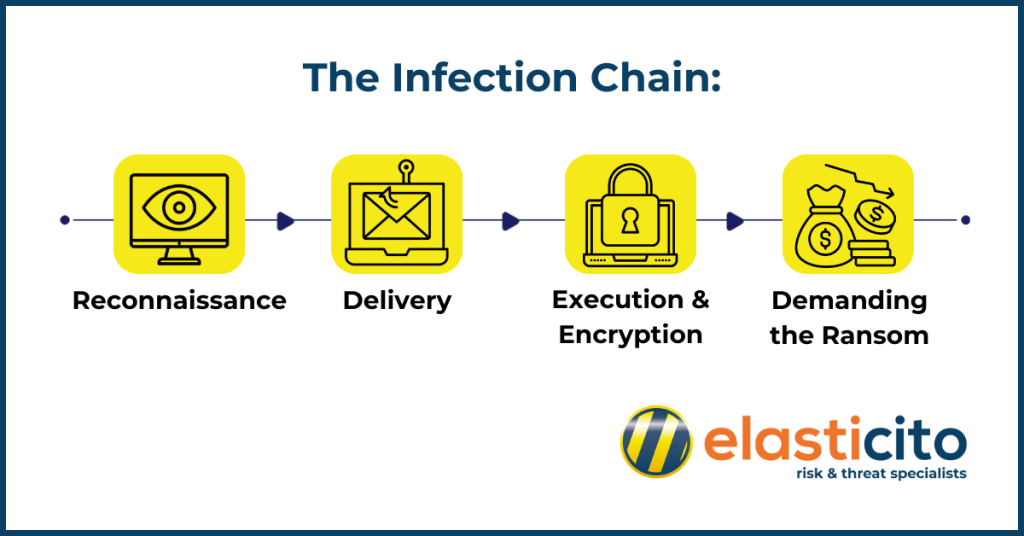
The Infection Chain:
- Reconnaissance: Before hackers launch an attack, they meticulously gather information. This initial phase, called reconnaissance, relies heavily on open-source intelligence (OSINT). Attackers scour the internet for details about your company, looking for vulnerabilities and weaknesses. They might find OSINT about misconfigured mail servers along with publicly available email addresses. Most importantly, they will search for known exploited vulnerabilities (KEVs) in your publicly facing infrastructure – weaknesses with readily available attack methods available. By uncovering these chinks in your armour, attackers can craft a targeted assault with a high chance of success.
- Delivery: Ransomware finds its way onto a system through various means, either through the exploitation of the above KEV’s, brute forcing of open ports like remote desktop protocol (RDP) or with phishing emails also being a common method. These emails often appear legitimate, tricking the recipient into clicking a malicious link or opening an infected attachment. Other vectors include infected websites, malicious software bundles, and even physical media like USB drives.
- Execution and Encryption: Once the Ransomware is downloaded, it executes on the victim’s system. The Ransomware encrypts operating system files, such as documents, photos, and financial records, and encrypts them using complex algorithms. This process makes the files inaccessible, preventing the user from opening or using them.
- Demanding the Ransom: After encryption, the Ransomware presents a message to the victim, informing them of the situation and demanding a ransom payment. The message typically includes instructions on how to pay, often using cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, which is difficult to trace. Ransomware attackers may also employ scare tactics, threatening to permanently remove the encrypted files or leak them online if the ransom is not paid.
Additional Tactics:
Modern Ransomware variants employ additional tactics to increase their impact:
- Lateral movement: The Ransomware may attempt to spread across a network, infecting other connected devices and servers. This significantly increases the attack’s impact and pressure on the victim to pay.
- Data breach: Some strains exfiltrate sensitive data before encryption, giving attackers leverage even if the victim chooses not to pay. This data can be used for further extortion or sold on the illegal market.
8 Surefire Shields Against Ransomware:
Falling victim to Ransomware can be devastating, both financially and emotionally. But fear not! Here are Elasticito’s top eight safeguards you can deploy to shield yourself and your organisations from Ransomware attacks and ensure the continued security of your data.
1. Patching applications:
Patches are like security updates for your software, fixing those vulnerabilities and making it harder for attackers to break in. OSINT can help identify emerging threats and attack methods.
Why do threat actors care? Here is what they are after
- Stealing data: Your personal information, financial details, or even company secrets could be their target.
- Taking control: Hackers might hijack your device to launch attacks on others or use its processing power for malicious purposes.
- Disrupting operations: A well-timed attack can cripple a organisations by taking down critical systems.
2. Implement an Impenetrable Backup System and Software Updates:
- Frequency: Daily backups are essential for critical data, while weekly may suffice for less sensitive information.
- Location is Paramount: Store backups on a separate device or platform, away from your primary system. Unmapped secured cloud storage or an external hard drive disconnected from your network are excellent options, as per recent reports highlighting the dangers of Ransomware attacks that target local storage.
- Test Your Shield Regularly: Do not be fooled by a false sense of security. Regularly test your backups to ensure they are functional and complete. This way, you can be confident they will work when disaster strikes.
Software Updates:
- Automate Updates: Many software vulnerabilities are exploited due to outdated systems. Leverage OSINT to track the visibility to Threat Actors and enable automatic updates whenever possible. This ensures your system stays patched and protected against known threats.
- Patch Management for Businesses: For organisations, a centralised patch management system streamlines updates across all devices. This minimises the risk of human error and ensures consistent protection across your network.
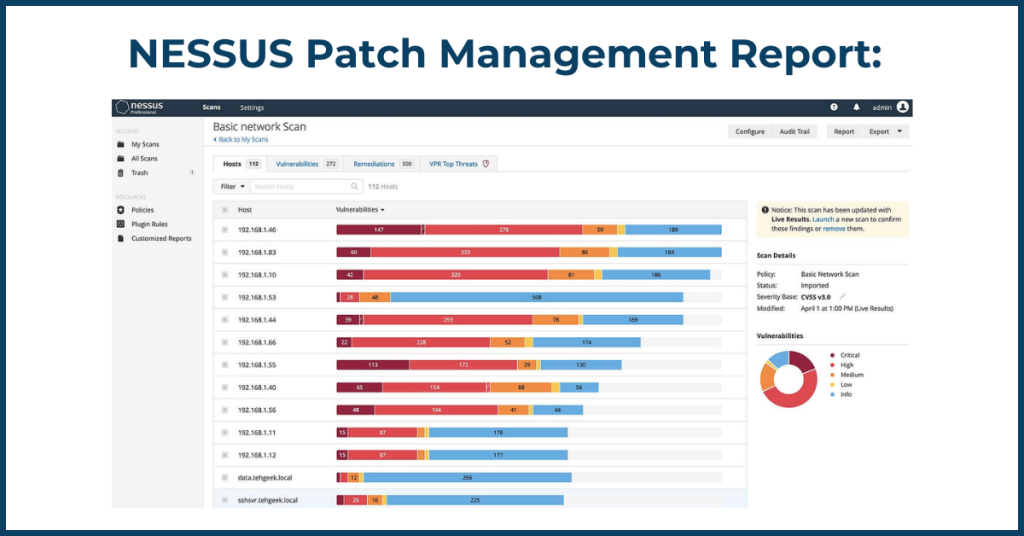
Source: NESSUS
3. Fortify Your Network Defences:
Your network acts as the gateway to your systems. Strengthening your network defences makes it harder for attackers to gain a foothold and deploy Ransomware.
Here are some key measures:
- Firewalls:A firewall acts as a barrier, filtering incoming, outgoing traffic, and blocking unauthorised access.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS): These systems monitor network activity for suspicious behaviour and can block potential attacks.
- Network segmentation:Divide your network into smaller segments to limit the potential impact of a breach. This ensures that if one segment is compromised, the entire network is not affected.
- Endpoint Threat Detection and Response (EDR): EDR continuously monitors devices for suspicious activity. It analyses data to identify potential threats, automatically responds to contain them, and provides tools for investigation.
- Web and Email Secure Gateways: Secure gateways function as shields for web traffic and email, filtering malicious content. They scan emails for threats and web traffic for malware, protecting users from online dangers.
4. Educate Users About Phishing Tactics:
Phishing attacks are a common method used by attackers to trick users into clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments that can deploy Ransomware. Educating users about these tactics is crucial to prevent them from falling victim to such scams.
- Train users to identify suspicious emails: Teach them to be wary of emails with urgent language, unexpected attachments, or requests for personal information.
- Hover over links before clicking: Encourage users to hover over links to see the actual URL before clicking. This can help identify spoofed links that appear legitimate.
- Report suspicious emails: Implement a system for users to report suspicious emails to the IT department for further investigation.
5. Passwords vs. Passphrases:
Consider using a password manager. These tools securely store your complex passphrases and automatically fill them in when needed, eliminating the need to remember them all.
- Passwords: These are typically shorter sequences of characters, often a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. The minimum recommended length is around 12 characters, though many fall short.
- Passphrases: As the name suggests, these are essentially longer passwords formed by combining multiple words. Ideally, passphrases should be at least 14 characters long, and often extend well beyond that.

Adapted from: Smashing Magazine
6. Employ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
MFA adds an extra layer of security to your login process. In addition to a password, it requires an added verification factor, such as a code sent to your phone or a fingerprint scan. This makes it significantly more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorised access, even if they obtain your password.
- Fortify login credentials: MFA transcends reliance solely on passwords. It introduces an added verification layer, requiring a second factor like a one-time code, fingerprint scan, or security key. This significantly bolsters login security, mitigating the risk of unauthorised access even if passwords are compromised.
- Safeguard sensitive data: MFA shields critical information like financial accounts, work documents, and personal details. By presenting an added obstacle for attackers, it significantly hinders their ability to gain access and potentially exploit your data.
- Enhance confidence and peace of mind: The knowledge that your accounts have an extra layer of security fosters peace of mind. MFA alleviates concerns about unauthorised access and potential data breaches, allowing you to use online services and applications with greater confidence.
- Straightforward and user-friendly: Most MFA methods are convenient and user-friendly. Popular options include receiving verification codes on your phone, using an authentication app, or using biometric options such as fingerprint or facial recognition.

7. Use Security Controls Validation Techniques:
A single penetration test or Red Team test once a year is generally not going to provide the validation of your security controls. That is why you should consider an automated Security Validation solution. These systems safely simulate the methods and techniques used by threat actors, like Ransomware groups, to regularly test if your security team and controls are able to detect and block Ransomware threats.
Here are some high priority MITRE ATT&CK Techniques that you should regularly test and harden or restrict for users who do not need to make use of them:
- PowerShell: Did you know that 70% of Ransomware malware is executed using PowerShell? If a specific role does not need this function, disable it and make sure that your monitoring and detections are tuned to identify abnormal use of PowerShell.
- Windows Command Shell: Similarly, Windows Command Shell is often hijacked by threat actors to execute their malware. If not required, disable or restrict it.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) ports: RDP ports are like leaving the back door of your house unlocked. They are often opened to allow particular traffic or to allow external contractors access to the network. However, they are also often unmonitored and left open. Threat actors can scan your externally facing infrastructure and identify open RDP ports; disable them if not in active use.
8. Have a Ransomware Recovery Plan:
Ransomware can cripple your data, but a plan can help you bounce back. Regularly back up your crucial information and store it securely, disconnected from your main network. Train employees to identify suspicious emails and avoid clicking unknown links. By planning and practicing, you can minimise downtime and protect your valuable data in the face of a Ransomware attack.
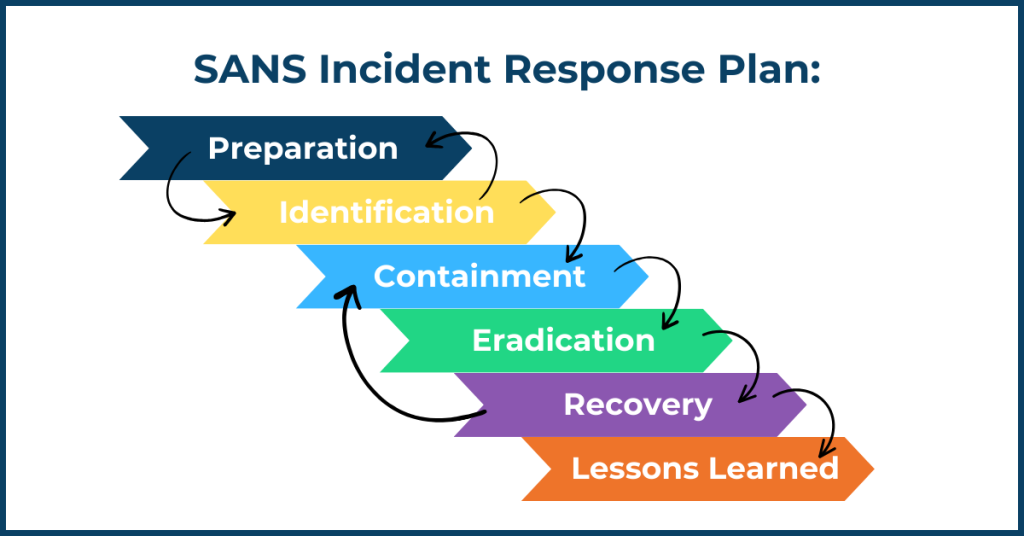
Adapted from: SANS Security Awareness
Additional Tips:
- Consider cyber insurance – here is a useful list of providers. In the event of an incident this will help offset the financial costs associated with a Ransomware attack.
- Be wary of opening attachments or clicking on links in unsolicited emails, even if they appear to be from legitimate sources.
- Regularly review and update your cyber security policies and procedures to ensure they still are effective in the face of evolving threats.
Conclusion:
Ransomware infiltrates systems through various means, including phishing emails, exploiting vulnerabilities, or malicious software downloads. Once inside, it encrypts your data and demands a ransom for decryption. To protect yourself, implement a layered security approach. Patch your applications regularly to address vulnerabilities. Create a robust backup system and store backups securely, disconnected from your main network. Regularly test your backups to ensure they are functional.
Fortify your network defences with firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, and network segmentation. Educate your users on phishing tactics to prevent them from falling victim to scams. Employ strong passwords or passphrases and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security to your login process. Consider using a password manager to store and manage your credentials securely. Regularly test your security controls using automated security validation techniques to simulate real-world attacks and ensure your defences are effective. Finally, develop a Ransomware recovery plan that includes regular backups, employee training, and clear recovery procedures.
Remove the target from you back and put Ransomware fears in your rearview mirror!
We hope our blog, “8 Surefire Shield Against Ransomware”, helps keep your data safe. Contact the team at Elasticito, obligation-free, to discuss Ransomware mitigation and security awareness training solutions.
